-
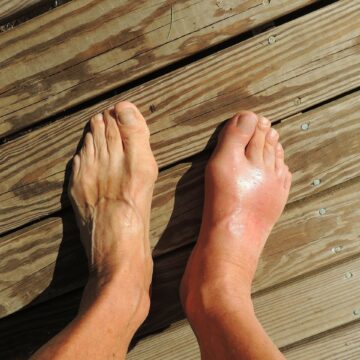
- Gout is a condition where there is a sudden and severe attack of pain and inflammation in the joints, especially the big toe.
- There are several known causes of gout, including diet, genes, medical conditions, and certain medications.
- Some lifestyle factors can also increase the risk of developing gout.
Gout happens when there is an accumulation of uric acid in the bloodstream, affecting the joints, including the big toe. A higher-than-normal level of uric acid in the blood is referred to as hyperuricemia. There are several identified causes of gout as well as the risk factors for developing it.
Below are some of these.
1. Diet

Gout is different from other forms of arthritis in that it is not an autoimmune disease. It is a condition that is caused by abnormalities in the body’s metabolism. The development of gout is greatly affected by diet. Foods contain an organic compound known as purine. In the body, purine is broken down and converted to uric acid, which is considered a waste product. The kidneys filter out uric acid from the blood and expel it from the body together with urine. When uric acid forms quickly but does not get excreted from the body, it can build-up in the blood. It can form into uric acid crystals that can cause gout attacks.
Several food and beverages can hasten the formation of uric acid in the body, and these include:
- Organ meats, bacon, veals, and certain seafood with high-purine content
- Beer – it contains a high amount of purine.
- High-fructose containing drinks like sodas and sweetened fruit juices
2. Genes

The genes can dictate the chances of developing gout. Mutations in the genes can lead to hereditary hyperuricemia and impairment of the kidney’s ability to excrete uric acid. Some genetic diseases can increase the risk for gout including hereditary fructose intolerance, medullary cystic kidney disease, Kelley-Seegmiller syndrome, and Lesh-Nyhan syndrome.
3. Medical Conditions

Some medical conditions can affect how the kidneys function, including their ability to excrete uric acid. Other conditions create an abnormal inflammatory response that can also affect uric acid production. These conditions can be:
- Anemia (hemolytic)
- Chronic kidney disease
- Congestive heart failure (CHF)
- Diabetes
- Excess abdominal fat
- High blood pressure
- Hypothyroidism
- High LDL cholesterol and low HDL cholesterol
- High triglycerides
- Infection
- Insulin resistance
- Lymphoma
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Surgery
- Traumatic joint injury
4. Certain Drugs

Some drugs can increase the concentration of uric acid in the blood or impair renal function. These are usually diuretic medicines like furosemide and hydrochlorothiazide. Parkinson’s disease drugs and vitamin B3 supplements may cause a spike in uric acid levels.
5. Lifestyle Choices

How you spend your day-to-day living can also contribute to the development of gout. Diet, excessive weight, and obesity can affect the frequency and severity of gout attacks. In one study, it was found out that those who have gout have more substantial abdominal fats. Their gout risk is also higher, which is almost 48%. On the other hand, those with regular waistline have only a 23.7% risk of developing gout. The study confirms that there is a direct link between waistline measurement and risk for gout. Excessive and regular alcohol use or being inactive can also increase the risk of gout development.
Source: Very Well Health
